
Between phones, appliances, industrial equipment and other devices, electronics have become a key part of our everyday lives. Each piece of equipment emits electromagnetic energy, which can interfere with other devices.
To ensure they all cooperate and work as intended, designers need to achieve electromagnetic compatibility (EMC). Many organizations have created EMC testing standards for certain products and industries. These tests address different aspects of emitted and absorbed energy and are a vital part of the design and distribution of electronics.
Thoroughly understanding EMC testing is key to producing electronics on schedule while meeting demands for performance, safety and compliance.
Table of Contents
What Is Electromagnetic Compatibility?
Electromagnetic compatibility refers to a device’s ability to work properly in a shared electromagnetic environment with other devices. It reflects the device’s resistance and contribution to electromagnetic interference (EMI).
Every electronic device emits electromagnetic energy that can affect other circuits. EMI comes from both human-made devices and natural sources, like lightning strikes and solar flares. If EMI reaches a circuit, it can cause problems that range from static on an audio line to disrupted power or a fried circuit board.
If a device has good EMC, it can work well alongside other electronics. EMC is the reason you can set your cell phone next to a computer or in your car without causing malfunctions. Some technologies used to achieve EMC include shielding and filtering components.
The three main components of EMC include:
- Emissions: This aspect assesses the energy a device generates and releases into its environment during normal operation.
- Susceptibility: Susceptibility refers to a device’s likelihood of malfunctioning or otherwise being disrupted when faced with EMI.
- Immunity: As the opposite of susceptibility, immunity shows how well a device can function when exposed to EMI.
EMC requirements can vary widely by device and market. A high-powered industrial motor may have far greater emissions allowances than a consumer-grade cell phone. Mission-critical devices, like medical and military equipment, typically have extremely strict susceptibility and immunity demands because they must stay operational at all costs.
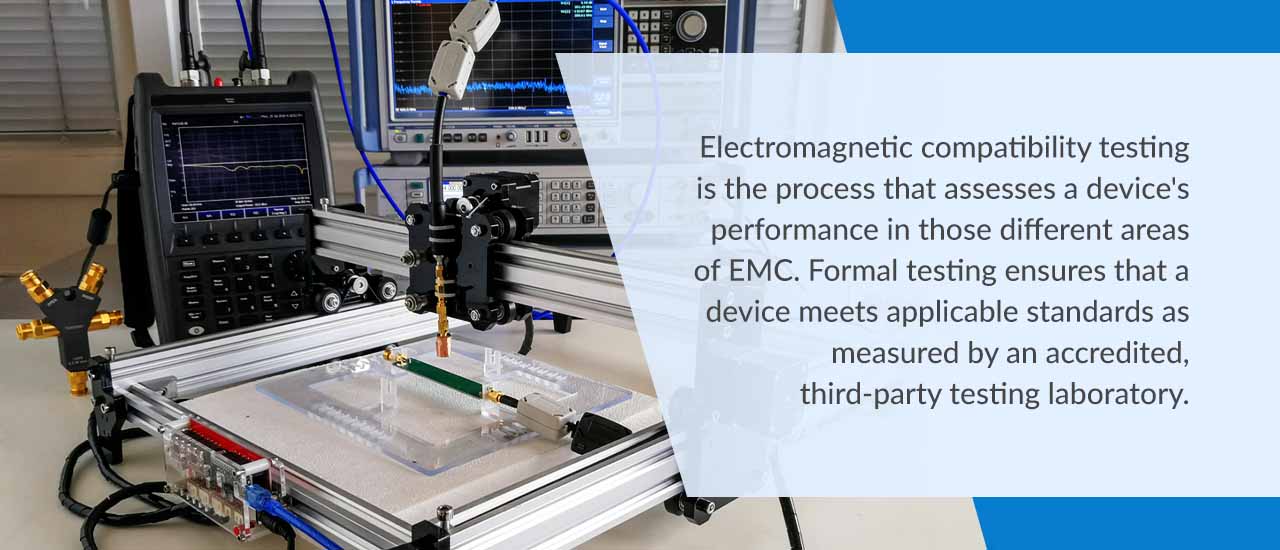
What Is Electromagnetic Compatibility Testing?
Electromagnetic compatibility testing is the process that assesses a device’s performance in those different areas of EMC. Formal testing ensures that a device meets applicable standards as measured by an accredited, third-party testing laboratory. Usually, these standards come from industry organizations and federal governments, such as the Federal Communications Commission in the United States.
Those organizations typically base their requirements on standards from international groups, which include the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) and the International Organization for Standardization (ISO). They are a major part of standardizing EMC testing and simplifying compliance across borders. Instead of obtaining new certifications for every country you want to sell a product in, you can often satisfy IEC or ISO standards and sell in many regions.
Sometimes, EMC testing is split up into different areas, such as susceptibility or emissions testing. For example, not all countries require immunity testing, so some devices may only need emissions testing to be compliant. Compliance requirements can vary widely by device and industry, but virtually every electronic must go through EMC testing before it can be distributed.
An EMC test might evaluate a device’s:
- Radiated emissions
- Conducted emissions
- Flickers
- Electrostatic discharge immunity
- Radiated radio frequency immunity
- Surge immunity
- Harmonic performance
Why Is Electromagnetic Compatibility Testing Important?
EMC testing is crucial from both business and safety perspectives. Of course, it wouldn’t be a requirement if EMC wasn’t important. Below are some of the reasons manufacturers must conduct EMC testing.
1. Safety
Our health and safety often depend on the performance of electronic devices. Medical equipment, for instance, has very clear ramifications — lives would be at stake if devices like ventilators or pacemakers malfunctioned. Similarly, interruptions to military, aerospace or industrial operations could also put public safety at risk. EMC testing is vital for ensuring these devices keep working in the presence of heavy EMI.
Even outside of high-stakes applications, moderate EMC helps keep consumers safe from malfunctions that could lead to heat, fire or shocks. It also helps provide dependable operation for crucial tasks like contacting emergency services.
2. Performance
EMI can quickly affect the performance of electronic devices. Testing assesses whether your device will function appropriately in an environment with EMI. From data corruption to errors and interruptions, EMC testing is critical for delivering a high-performing product that meets the needs of end users.
It also helps businesses avoid reputational damage that might come from poorly performing products. For example, a product that always overheats because it wasn’t tested in the right environment could hurt your company’s image. If safety issues arise, the effects could be even more pronounced. In comparison, good EMC may give you an edge over the competition.
3. Compliance
EMC testing is the best way to avoid hefty fines and penalties from government or industry organizations and civil or criminal lawsuits. Comprehensive testing provides clear, objective data about the characteristics of a product.
It can also offer risk mitigation by helping you avoid penalties and losses from withdrawing products from the market. Without compliance, products could be recalled or cause more serious problems, such as safety issues.
Good testing can also help you avoid expensive, last-minute changes by identifying EMI issues early. You can make modifications long before your product hits the shelves rather than scrambling to meet time-to-market deadlines.
What Is Electromagnetic Compatibility Certification?
As you might expect, an EMC certification shows that a product meets certain EMC specifications. These certifications may be issued by testing labs if you meet the appropriate criteria. For instance, IEC 60601-1-2 is recognized internationally and tests emissions and immunity for medical devices. Any products submitted to the U.S. Food and Drug Administration or the European Union must meet IEC 60601-1-2. An accredited lab can issue a certification.
Many countries require some type of certification before businesses can sell electronic devices in the region. By requiring certification, the country helps prevent unsafe products from entering circulation. You’ll typically need EMC certification for medical, military or aerospace devices in most countries. Many consumer goods also require certifications, particularly the following items:
- Cell phones
- Consumer appliances
- AC adapters
- Laptops
- High-intensity lights
- Electric motors
Achieve EMC With AerosUSA Wiring and Cable Systems
Whatever your product looks like, you’ll need the right components to ace an EMC test. From protective conduits to sealed connections, high-quality components are crucial for minimizing EMI and obtaining EMC certification.
AerosUSA is a trusted solutions provider with considerable expertise in electrical engineering and specialty materials like polyamide technology. We offer a wide range of cable and wire protection products, so you can protect your equipment from EMI and prevent excessive emissions, all while meeting specifications.
Our knowledgeable team can help you find the right solution to tackle EMI, so you’re ready for EMC testing and quickly get your product certified and on the shelves. To talk with a pro about our EMC products, reach out to us today.


